Telecommunication#
Fundamentals#
primitive example: two people talking to each other
communication system

Exercise 17
\(r(t) == s(t)\) ?
In words: Does sent data typically equal to the received data?
- distortion
the alteration of the original shape of a signal
Exercise 18
Which of the examples are distortions?
my mother cannot hear high frequencies
the sound interface clips amplitudes higher than 5V.
speaking with heavy cold
Degradation examples
additive noise: new unwanted content added to the sent info
e.g., two people talk in parallel and you have difficulties understanding one
distortion: original content changes
e.g., your talking partner caught cold
attenuation: weakening of the signal over the distance
e.g., your talking partner is far away
\(r(t) = s(t) + n(t)\)
noise is added to the signal on the way
filter added to remove the noise
the channel can be fiber, copper, air etc
example goal: carry as much info as possible
Shannon–Hartley theorem describes the max transmission speed given the noise
- transceiver
a device which is a combination of a transmitter and receiver
Wired vs wireless#
Exercise 19
Do you prefer wireless or wired headphones? Why/ why not?
wireless: 1790s Chappe telegraph
wired using electricity: 1840s electrical telegraph
- Line-of-sight (LoS) propagation, primary source
a characteristic of electromagnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation which means waves can only travel in a direct visual path from the source to the receiver without obstacles.
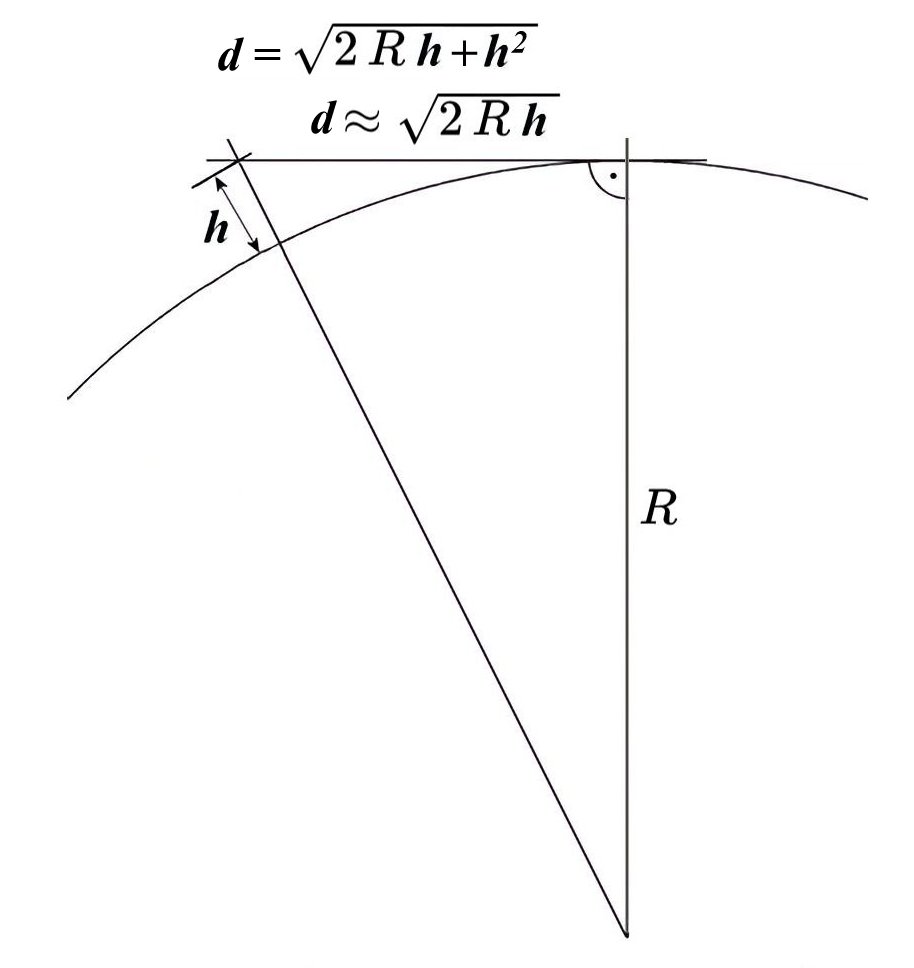
Fig. 9 Calculation of an antenna’s LoS horizon. There is a point around the antenna where a straight line eventually becomes a straight line, which is \(d\) away from the antenna. \(R\) is the earth radius.
CC BY-SA 4.0. By FBuHL09. Source: Wikimedia Commons#
Exercise 20
LoS propagation states that we need LoS to communicate. How can we get stay connected with a base station even we are in a building or receive radio signals from far away?
Wired communication using light: 1800s, basis for optical fiber
Exercise 21
What is the most significant advantage of wired communication compared to the wireless?
Electrical wireless
1880s: first telephone
end of 19. century: radio broadcasting
1930s: television broadcasting
one-way communication, simplex
1979: Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) - 1G
1991: 2G, short messaging service (SMS)
3G, multi-media messaging service (MMS), video calling, internet surfing
can complement traditional wireless by using other frequency bands
can use existing infrastructure like street lights
more secure, as LoS required
can use existing infrastructure
Exercise 22
What could guided and unguided media in our context mean?
Exercise 23
Think about wired and wireless communication. Which is more advantageous in telemedicine?
Exercise 24
Assume you are using a tin can telephone.
The communication medium is …
It is a (guided/unguided) medium.
Explain modulation in this context, e.g., what is modulated on what?
Conducting vs optical cables#
typically used in the networking backbone
- Backbone network
part of a computer network that interconnects networks, e.g., LAN.
Exercise 25
How do we transmit a signal or information over a conducting/optical cable?
fiber optic cables
glass: higher transmission rates
plastic: cheaper, but bendable
Data transmission speed#
- Bandwidth (computing)
Maximum rate of data transfer across a given path, typically measured in bit/s
Bandwidth (computing) is in contrast to the analog signal bandwidth. Analog signal bandwidth is the frequency range between the lowest and highest attainable frequency, e.g., analog telephone signal 300 Hz to 3400 Hz has a bandwidth of 3100 Hz
- Baud
unit for symbol rate. Number of signal state changes per second
named after Baudot, French engineer
Exercise 26
What is the difference between symbol rate and bandwidth?
Exercise 27
A communication line supports 9600 bits/s. Each symbol uses 5 bits. What is the symbol rate?
Exercise 28
You use five different signal levels to encode a symbol using binary coding. What is the average bit rate over the channel that has 1000 Baud?
Exercise 29
What is a symbol in telegraphy using Morse code?
Describes the maximum achievable bandwidth over a communication channel without any noise.
\(C\): Channel capacity or maximum data rate (bits per second)
\(B\): Bandwidth of the channel (Hz)
\(L\): Maximum number of achievable signal levels
\( L = {1 + \frac{S}{N}} \)
\(S\): signal power
\(N\): noise power
intuition
we need +1 to have at least one signal level, even noise is too high. So in worst case, we have a channel capacity of zero, because \( \log_2(1) = 0 \).
Related to the Nyquist-Shannon theorem: we have to sample more than the double of the channel bandwidth to recreate a signal.
Fig. 10 Relation between: (1) channel bandwidth (2) Nyquist frequency (3) Nyquist rate (4) Sample rate
CC0. By Bob K. Source: Wikimedia Commons#
Exercise 30
You want to maximize the capacity over a communication channel. What can we derive from equation (1)?
Exercise 31
Imagine you are an engineer and designing a communication line between two locations. How could Shannon-Hartley theorem support you?
Electromagnetic interference (EMI)#
- Electromagnetic interference (EMI)
disturbance of a signal due to electromagnetic waves in the environment
EMI is more of an issue for wireless than wired
wires typically have insulation
guiding provided by the cable itself provides some protection
Example: mobile phones used to be forbidden in the airplanes due to EMI
nowadays the airplanes probably have better EMI shielding, the effects are less than expected
the airplane mode still exists probably to prohibit your phone to needlessly communicate with mobile stations and consume battery.
Types of EMI
continuous
e.g., a switching power supply at a constant load
transient
thunderstorm
- CE marking conformité européenne, European conformity
a stamp that allows the good be traded freely in the EU

Fig. 11 Typically every sold device has a CE label.
CC BY-SA 4.0. By Raimond Spekking. Source: Wikimedia Commons#
Most electrical products must be tested for electrical safety and EMI to get the CE label.
medical devices must conform to the corresponding EU regulation
Exercise 32
Look on one of your USB charge adapters. Do you see a CE logo? Why is it there?
Modulation#
- Modulation
process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a separate signal called the modulation signal that typically contains information to be transmitted
You have a carrier signal
e.g., 5V signal on a cable you alter certain parameters to represent data
e.g., pulse width modulation to create an sine signal using a microcontroller

Fig. 12 FM (frequency modulation). FM modifies frequency according the the voice information.
CC BY-SA 2.5. By Berserkerus. Source: Wikimedia Commons#
Example modulation parameters other than frequency
amplitude
phase
- Spectral efficiency
a measure of how efficiently a limited frequency spectrum is utilized. We divide bit rate by the available bandwidth. In other words, we normalize the bit rate for comparing it with other kinds of channels.
The result is in bit/s/Hz. We could interpret it as number of bits that we can send per cycle (of the used frequency).
Also called spectrum- or bandwidth efficiency.
Spectral efficiency is a bandwidth-independent metric
max bandwidth is given by the Nyquist theorem
\(2 \cdot N \cdot n_\mathrm{symbols}\), where the variables are the bandwidth and number of symbols, respectively.
we get rid of \(N\), because spectral efficiency is independent of bandwidth:
\(2 \cdot n_\mathrm{symbols}\)
Exercise 33
A V.92 modem for the telephone network can transfer 56 kbit/s downstream over an analog telephone network. Due to filtering in the telephone exchange, the frequency range is limited to between 300 Hz and 3,400 Hz, corresponding to a bandwidth of 3400 − 300 = 3100 Hz.
What is the modulation efficiency?
What does the result mean?
See some examples on the comparison table on Wikipedia:
For example:
Even 1G and 2G cellular based on AMPS and D-AMPS had the same bandwidth per carrier, the second generation achieves much higher efficiency. Probably due to the choice of modulation techniques.
We see similar difference between LTE and LTE-Advanced.
Different kinds of services for telecommunication#
Fig. 13 Diagram of OSI model. Each layer plays an individual role in telecommunication. Media layers are important when the communicated data is transferred over the media (e.g., air, cable). Host layers are important for transferring data on a computer (host).
Public domain. By Offnfopt. Source: Wikimedia Commons#
OSI model does not mean that all these responsibilities should be separate. It is just a representation of different services that are typically used for communicating data between devices.
For our learning goals, understanding the following layers is sufficient:
Data Link
Physical
- Physical layer
provides an electrical, mechanical, and procedural interface to the transmission medium.
Topics associated with the physical layer:
bit-by-bit or symbol-by-symbol delivery over the physical medium
mechanical specification of components, e.g., max. cable length
electrical specification of line signal level
electromagnetic spectrum, e.g., frequency allocation
how data is converted into a digital signal, also called line code
network topology, e.g., mesh, star network
- Data link layer
provides the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities and may also provide the means to detect and possibly correct errors that can occur in the physical layer.
Two sublayers:
-
automatic repeat request
error correction
managing the rate of data transmission (flow control)
-
how can multiple devices access the medium, e.g., collision avoidance in wireless (CSMA/CA)
physical addressing (MAC addressing)
Other aspects associated with the data link layer:
encapsulation of data into frames
frame synchronization
Physical and data link layer specifications are typically provided by standards, e.g.,
IEEE 802.3 for Ethernet
IEEE 802.11 for Wi-Fi
3GPP release 18 standard for 5G
